Security Glossary of Terms
2.4G Wireless
2.4G is short for the 2.4GHz radio frequency band used in Wi-Fi routers. The 2.4G band will provide longer range than the newer 5G band but cannot handle the same amount of bandwidth (channels) as 5G. It also is more likely to be affected by external interference like devices using Bluetooth, ZigBee, and cordless phones .
5G Wireless
5G is short for the 5GHz radio frequency band used in Wi-Fi routers. The 5G band has higher bandwidth (more channels) than the older 2G band so it can provide much faster downloads, uploads and video streaming. However, it's range (distance coverage) is less than the 2G bands (almost 50% less).
Ampere Hours (Ah)
An Ampere Hour or amp hour (Ah) for short is a unit of electric charge. In simpler terms its the number of amps (current) a battery will provide per hour. One AH would be 1 Amp for one hour. In the security world its used to describe the backup capacity of a system. To use an alarm system as an example. If your alarm uses a continuous one (1 ) amp of current in normal operation, there is a 7Ah battery installed in the Control Panel and there's a power outage. The alarm will continue to operate for approx. 7 hours.

Backup Battery
Typically placed inside in the Control Panel and is used to provide power to the system during a power outage. They are rechargeable so once the power has been restored the control panel will replenish its charge. Batteries come in many different sizes and are measured in Ampere Hours (Ah). Typical battery life would be approx. 3-5 years but some have been known to reach 10+ years. Checking these batteries should be part of a regular maintenance routine.

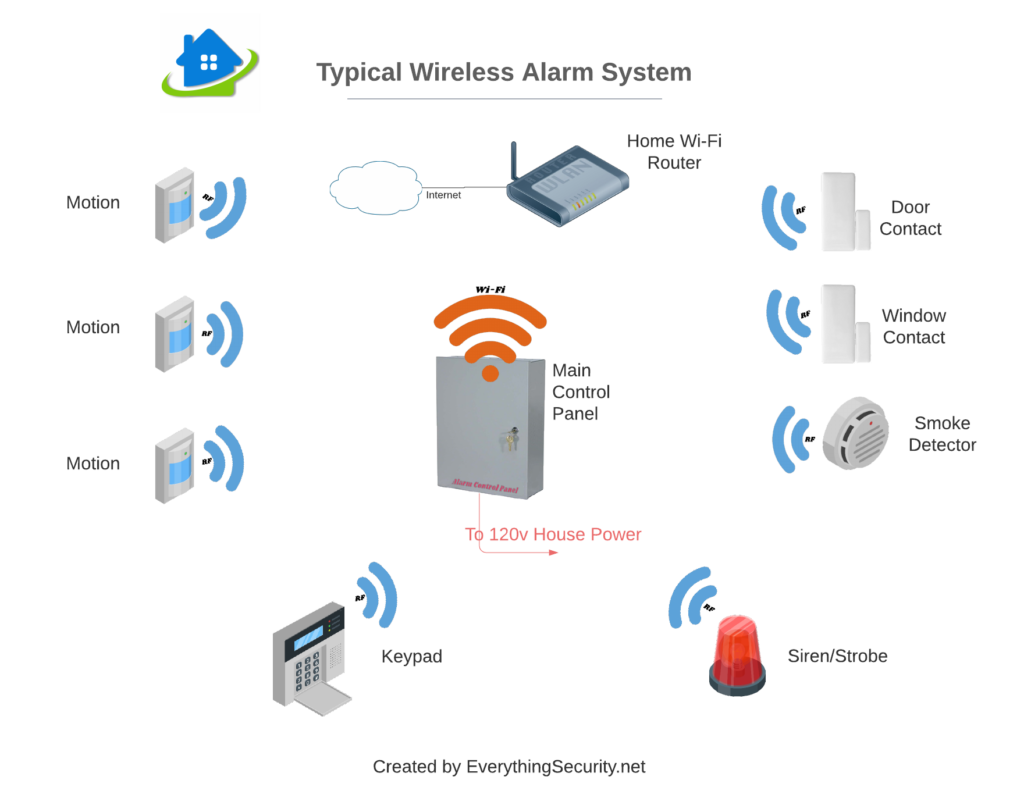
Burglar Alarm System
An electronic system consisting of a Control Panel/HUB, detection sensors and Keypads and or Touch screens. Systems can activate sirens and/or strobes and be monitored remotely. Used to detect unauthorized entry into a premise.

Control Panel
A Control Panel is considered the brains of an alarm system. It will typically will take the form of a small metal enclosure that houses an electronic circuit board inside. This is where you would wire in sensors (if a hardwired system), connect keypads, install the backup battery and connect to household power. Optional or specialized circuit boards are also installed inside this control panel. It will in many cases have a lock on the door to prevent unauthorised entry.
Cellular Monitoring
Alarm Systems that use Cellular Monitoring means that it is using a digital cellular network to send alarm, trouble and supervisory messages to a remote Monitoring Station system. The system uses a cellular communicator normally inside the control panel to send signals.

FOV
FOV stands for Field of View. This term is used in multiple areas in security. For Motion Sensors it describes the area that a Motion can detect movement. For Cameras it's the area that can be seen by the camera.
Frames per Second (FPS)
The frame rate measured in Frames per second. This is the rate at which images are captured or displayed. Used with video cameras to describe how many frames (images) are being captured per second. A video camera set to 30FPS means it is capturing the image/scene at 30 images per second.
GPRS - General Packet Radio Service
A data packet oriented data standard used on the 2G and 3G cellular communications networks. It is an enhancement to the standard GSM network infrastructure. It provides for moderate speed data transfer. 2G is almost all but phased out (service no longer available) and 3G is is in the process of being phased out by the major carriers.
GSM
The Global System for Mobile (GSM) is a international standard that defines the protocols used with digital cellular networks . It is a 2nd generation technology (2G) and is almost all but phased out (service no longer available) in US and Canada. GSM was a digital cellular technology used to transmit data and voice communications at a frequency range between 850MHZ and 1900MHZ.
Hardwired System
A Burglar Alarm system that uses wires and cables to connect it's devices to the main Control Panel.

Mesh Network
A mesh network allows each device in a network to operate as a repeater and pass the signal on to another device. This causes mesh networks to be more versatile. They cover greater distances and can even work around obstacles.
Mesh Hop
A wireless mesh network is a network where the nodes in the network communicate with other nodes to achieve increased coverage and connectivity by forwarding messages on behalf of others.

Monitoring Station (MS)
Monitoring Stations or Centers are facilities that monitor alarms, troubles and supervisory events from security systems. When an event is received by a MS trained operator they will dispatch the appropriate authorities and/or depending on the event contact the customers representative (pass card holders). Monitoring Stations run 24 hours a day and provide all the automated computer systems to be able to handle 1000's of alarm per day. Depending on what type of monitoring is being provided a MS may be listed with organizations such as UL, ULC. If listed it means that they have demonstrated compliance to the strict monitoring station requirements of theses organizations. Ongoing audits are conducted by these organizations to ensure ongoing compliance.

Motion Detector/Sensor
Motion Detectors are also called Motion Sensors or just plain Motions. It is a device that detects movement of objects in it's field of view (FOV). They come in many shapes and can use different technologies to actually sense movement. The most common type of Motion is a Passive Infrared Sensor (PIR). It uses an electronic sensor inside that measures the amount of infrared (IR) light coming from a object. It also uses electronics inside to determine if the amount and type of movement is enough to trip the sensor. Other technologies used include Microwave and in the old days Ultrasonic. Nowadays Ultrasonic detectors have been replace with PIR but is still used in may other industries.

IP Camera
IP (Internet Protocol) Camera refers to digital cameras that transmit their video over a IP based network. They are typically connected using a standard Ethernet cable (cat5 or cat6). They can also use Wi-Fi instead of a hardwired connection to transmit it's video. IP Cameras typically provide higher resolution video as compared to their Analogue counterpart. The power needed to operate an IP Camera could be provided using POE (Power Over Ethernet) or separate power cables. However, in order to use POE both the camera and the network device (router) its connected too must support POE.
IR
IR stands for Infrared radiation. It is a type of radiant energy that's invisible to human eyes. All objects radiate some amount of IR but Humans and animals radiate a good amount. That's why PIR's use IR technology to detect people. It is sometimes referred to as the Heat being radiated from a human body.
PIR
PIR stands for Passive Infrared. It is a type of sensing technology used in Motion Sensors that detects movement using the Infrared Energy (IR) being radiated from an object. See Motion Detector/Sensor.
POE - Power Over Ethernet
POE is a technology that allows the powering of network devices, like IP cameras, over the same network cable used to send/receive network communications for the device. In the security industry this is used mostly when using IP Cameras but can also be used with other devices.
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that allows the storage of digital data inside a Tag, Key Fob or Card which can then be captured by a reader using radio waves. RFID devices are typically made of durable plastic and contain an integrated circuit and an antenna. There are Active Tags and Passive Tags. Active Tags have built-in power (battery) while Passive Tags are powered-up by the RFID reader. When a Passive Tag is presented to a RFID reader they receive power (from the reader) and in turn will transmit the data contained inside.

SIM Card
SIM stands for Subscriber Identity Module. A SIM Card is basically a integrated circuit running a Card Operating System (COS) Operating system. It stores the identity of a subscriber and is used to authenticate on a mobile phones, satellite phones, smart watches, computers and other devices. It also stores carrier specific information. There are three different types of SIM's. Standard, Micro and Nano. Both the Standard and Micro are rarely used these days. Nano SIM cards are by far the most widely used.
Streaming
The act of transmitting video and audio files (media) continuously over a wired or wireless network. It is a delivery method not the content.
ULC - Underwriters Laboratories of Canada
Underwriters Laboratories of Canada (ULC) is an independent product safety testing, certification and inspection organization. They accredited by the Standards Council of Canada. ULC set requirements for Monitoring Stations
Wireless System
A Burglar Alarm system that does not use wires and cables to connect it's devices to the main Control Panel. Devices communicate to the Control Panel using Radio Frequency (RF).